
Summary
This project was performed with the aim of implementing a face recognition algorithm using an approach of eigenfaces. The algorithm was implemented using Matlab and tested with modifications on the images such as scaling, rotation and change in tone values.
The algorithm was extended and tested with images of the same people, but in more difficult environments. The images in this extended testing were also photographed under changes in lightning conditions, with different facial expressions, with blurred faces and with clustered backgrounds. With the extension to different facial expressions, the training set of the algorithm was extended and the eye detection updated.
Technical Walkthrough
Face recognition and face detection is a research area with a broad range of applications. Face recognition can be used in everything from unlocking a smartphone to the identification of people passing through a security gate. Since the applications are largely varied, the choosing of algorithm and approach is strongly connected with the desired product.
Using faces for recognition and identifying means that each person is described using characteristics that they carry with them all the time. It is a complex but distinct way to describe a person, although still facing difficulties when it comes to separate people that look a lot like each other. In the lack of universal solutions, the designer of a face recognition algorithm will most likely have to consider weather it is of most importance if the algorithm should minimize false positives (that persons who should not be classified, are classified), or false negatives (persons who should be classified are not).
This project uses one possible approach for the implementation of a face detection and recognition algorithm with focus on working well in a closed environment. The face recognition algorithm is implemented to work on loaded images, and not in real-time, which adds additional aspects within image processing to correctly identify the person in the image. Therefor the algorithm is extended and tweaked for working with images that have a larger variation in light and environment setting and addresses some difficulties that a face recognition algorithm needs to take into consideration.
The methods used in this project are PCA and eigenfaces. In this way, it is possible to find the principal components of the distribution of a face and bring these together as a set of features.
The eigenfaces method is the recognition part of the algorithm, but before it is possible to use the eigenfaces it is needed to adress the problems regarding the variation that can be seen in a face if it is scaled, rotated or under influence of different light. Therefor a solid face detection algorithm is needed to first make sure that the eigenfaces can be compared.
Face Mask
The usage of the face mask is to only keep relevant areas usable for the face detection algorithm by masking out the face. The face mask is created by finding the skin tone for humans in the image. Since the skin tones in the face is better described with YCbCr than RGB values, the image is converted into the YCbCr color space. This color space is described by a luma component, Y, and the blue-difference component, Cb, and the red-difference component, Cr. Thresholds are used to limit all channels individually so only the skin color area are kept in the image

Facemask
The area for the skin color is made into a binary image which is the foundation for the mask. Morphological operations are then applied to the image to clean it from small irregularities. The operations used are in following order opening, closing, dilation. A flood fill algorithm is then used followed by erosion which becomes the final mask
Eye Map
A good way to identify a face is to find the eyes. An eye map can be produced using the fact that the eyes has tones which are distinct from the rest of the face. The approach used is to combine two separate methods of making a eye map because with the use of two methods, the chances of finding the eyes will increase. The two maps are using information inside the chrominance component and the luminance component of the image.
Because of the large contrast in the luminance in the white areas in the eyes, this can be used with morphological operations to make the luminance even stronger. The image is converted into a gray scale image and then the following operations are used to strengthen the eye features.
To get the chrominance, the RGB-channels in the image has to be converted into YCbCr color space. The main idea behind the chrominance method is to enhance the eyes by using that in the eyes, we have high values in the Cb channel and low values in the Cr channel.
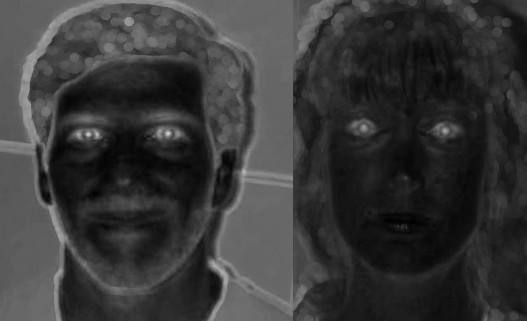
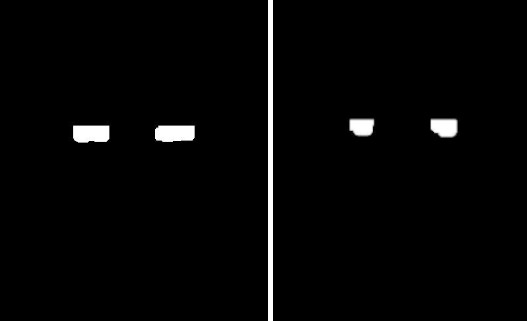 Eye maps, before and after morphological operations
Eye maps, before and after morphological operations
Eye Detection
The actual detection of eyes and deciding their coordinates in the image can be done in a multiple of ways, and as mentioned before, especially the combination of approaches can give additional security. In the algorithm in this report, the eyes are represented as two points inside the image, one for the left and one for the right. The best possible representation of the eyes are found when the point is in the center of the pupils for both eyes.
The first thing is to create an association between all pixels and its corresponding area in the mask. Then all pixels for each area inside the mask is counted and the areas are sorted depending on how many pixels it has. The two areas that contains the largest amounts of pixels are chosen as the eye candidates and the other ones are ignored. The mean value for all pixels in those two areas are calculated, which then are used as points to represent the eyes positions.
Since the eyes are found by using mean of the pixels in an area surrounding the eyes, the position is not exactly at the middle of the pupil. To get the exact position, circles are searched for in the face by using a circular Hough transform on the gray scale image. If a circle is found and it is close to the point that was received using the mean method, the position is moved to the center of that circle.
Image Transformations
When the eye candidates have been found, it is time to prepare the images for the face recognition part. For the eigenfaces to work well, the image has to fulfill some criteria before using them. All images has to be the same size. The faces in the images has to be aligned and only the face should be inside the image and no disturbing background should exist.
For rotation, an angle has to be specified for how much the image needs to be rotated such that after the rotation, the eyes in the image are placed horizontally. To achieve this, two vectors that are based on the position of the eyes in the image are used. The first vector is defined from the right eye to the left eye and the second is defined to start at the left eye and end at a position right to the first position, with the same height. The angle between those vectors are the corresponding angle that determines how much the image has to be rotated to set the eyes horizontal.
The scaling of the image is applied to make all images have their center at the same position. A value for the desired amount of pixels between the eyes are set, and the rotation is applied to the image. Since the eyes now are horizontally placed, the distance between the eyes are the same as the amount of pixels between them. With that knowledge, the scale factor can be found by dividing the number of desired pixels between the eyes by the distance between the eyes in the image.
Lastly, all images are cropped to get the same width and height, and only contains the face region. Since the images already are scaled and rotated, all images will be aligned correctly if the same point in the face are set as a mid point to crop the image around. The position is chosen to be the point precisely between the eyes, and then the width and height are chosen so that the entire face is inside the cropped result.
Light Compensation
Since the methods for making eye maps and face masks is dependent on the colors in the face, it is important to neglect any color coming from the light source that may influence the perceived skin color. To remove the color contribution from light sources in an image, gray world compensation is implemented and applied.

Face mask in insufficiant light conditions before and after light compensation
PCA and Eigenfaces
All images in the database are stored into 1-dimensional vectors where each vector has a size of width*height. These vectors are then used to calculate the mean image vector, which is the mean value of all faces combined.
The eigenvectors for the images are made from calculations of the covariance of the difference of all image vectors and the mean image vector (D). The database of images has to be prepared where vectors for eigenfaces, mean image and weights are calculated to have something to compare the input images with. These vectors can be stored once calculated and used for every test.
The eigenvectors and weights are calculated and to being able to compare the images with each other, the images can then be compared by calculating the Euclidian distance between the weights. If the input image is below a certain threshold, the image is concluded to be in the database and a match is found, else the algorithm returns 0. For the closed database of 16 images, a success rate of 88% is determined for the algorithm.

Visualization of eigenfaces